鄭瓊娟教授(兼所長科主任)
Chung Jiuan Jeng, Ph.D. Professor
實驗室介紹
歡迎來到我們的實驗室!我們目前有兩個研究方向:(1)離子通道疾病,(2)神經發炎的訊息機制。藉由了解疾病的病生理機制,期待未來可以研發出預防及治療這些疾病的方式。
實驗室研究方向
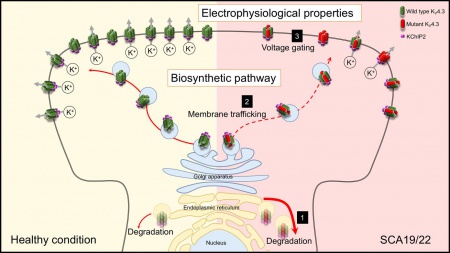
神經細胞有許多不同種類的電位控制鉀離子通道,這些鉀離子通道是設定細胞膜興奮性、設定細胞活化頻率、型塑動作電位波形和調控神傳導物質及荷爾蒙分泌等功能所必需的。目前實驗室的研究結合了分子生物學、生物化學、細胞生物學和電生理等技術,探討離子通道的構造與功能,研究離子通道蛋白質生合成與降解的衡定調控機制,及研究離子通道突變引發神經系統疾病的分子機制等。我們主要研究方向之一是探討ether-á-go-go(Eag)鉀離子通道的構造與功能,並藉著研究與疾病相關的Eag1和hErg突變蛋白質的衡定調控,以了解EAG鉀離子通道在神經細胞的正常生理與病生理角色。另一研究方向的主角是Kv4鉀離子通道,主要探討和脊髓小腦性共濟失調症(SCA19/22)相關之Kv4.3突變蛋白質的分子特徵,研究SCA19/22相關的Kv4.3突變蛋白質對正常型蛋白質造成的影響,包括如何影響正常型Kv4.3蛋白質的合成、降解、膜運輸、電壓依賴門控等的分子機制。除了與多位老師合作探討細胞內訊息傳遞路徑,本實驗室也參與在學校的腦科學中心的研究團隊中,利用培養的神經細胞與基因剔除小鼠,以分生和細胞生物學的方法,結合免疫螢光染色和共軛焦顯微鏡的觀察,研究神經細胞中分子的分布和變化,探討影響神經細胞生長、死亡、興奮性的因子,及神經細胞受到傷害時的保護機制等。
教師資訊
鄭瓊娟教授(兼所長科主任)
現職
- 陽明交通大學解剖學及細胞生物學科暨研究所教授
學歷
- 加州大學洛杉磯分校解剖學及細胞生物學研究所博士
- 臺灣大學醫學院解剖學研究所碩士
- 臺灣大學醫學院物理治療學系學士
經歷
- 輔仁大學醫學系助理教授
- 台醫生物科技公司研究員
- 美國加州理工學院博士後研究員
- 美國加州大學洛杉磯分校博士後研究員
- 臺灣大學醫學院解剖學研究所助教
重要獎項與榮譽
- 陽明大學106學年度校級教學優良獎
- 陽明大學100學年度醫學院教學優良琉璃獎座
- 陽明大學97學年度校級教學優良獎
研究專長
- 離子通道、細胞生物學、神經科學
發表論文
- C.-H. Hsieh, C.-C. Chou, Y.-C. Fang, P.-H. Hsu, Y.-H. Chiu, C.-S. Yang, G.-M. Jow, C.-Y. Tang, and C.-J. Jeng* (2023) 14-3-3 proteins regulate cullin 7-mediated Eag1 degradation. Cell & Bioscience 13:18. doi: 10.1186/s13578-023-00969-w.
- L.-H. Changa, N.-F. Chib, C.-Y. Chen, Y.-S. Linb, S.-L. Hsub, J.-Y. Tsai, H.-C. Huang, C.-J. Linb, C.-P. Chung, C.-Y. Tung, C.-J. Jeng, Y.-C. Lee, Y.-T. Liu, I.-H. Lee* (2022) Monogenic causes in familial stroke across intracerebral hemorrhage and ischemic stroke subtypes identified by whole exome sequencing. Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology, doi: 10.1007/s10571-022-01315-3.
- Y.-L. Gan, C.-Y. Wang, R.-H. He, P.- C. Hsu, H.- H. Yeh, T.- H. Hsieh, H.- C. Lin, M.- Y. Cheng , C.-J. Jeng, M.-C. Huang* and Y.-H. Lee* (2022) FKBP51 mediates resilience to infammation-induced anxiety through regulation of glutamic acid decarboxylase 65 expression in mouse hippocampus. Journal of Neuroinflammation 19:152. doi:10.1186/s12974-022-02517-8.
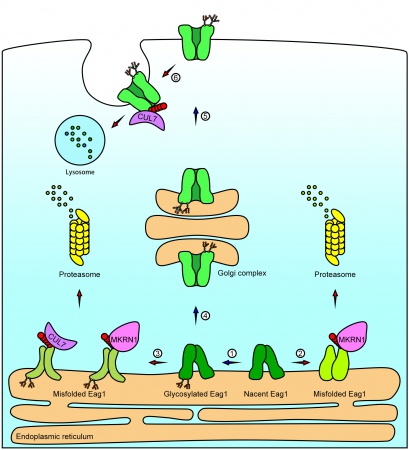
- Y.-C. Fang, S.-J. Fu, P.-H. Hsu, P.-T. Chang, J.-J. Huang, Y.-C. Chiu, Y.-F. Liao, G.-M. Jow, C.-Y. Tang*, and C.-J. Jeng* (2021) Identification of MKRN1 as a second E3 ligase for Eag1 potassium channels reveals regulation via differential degradation. Journal of Biological Chemistry 296, 100484.
- C.-T. Hsiao, T.F. Tropea., S.-J. Fu, T.M. Bardakjian, P. Gonzalez-Alegre, B.-W. Soong, C.-Y. Tang*, C.-J. Jeng* (2021) Rare gain-of-function KCND3 variant associated with cerebellar ataxia, parkinsonism, cognitive dysfunction, and brain iron accumulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 22, 8247. doi: 10.3390/ijms22158247.
- G. Zanni*, C.-T. Hsiao, S.-J. Fu, C.-Y. Tang, A. Capuano, L. Bosco, F. Graziola, E. Bellacchio, S.. Servidei., G. Primiano., B.-W. Soong and C.-J. Jeng* (2021) Novel KCND3 variant underlying nonprogressive congenital ataxia or SCA19/22 disrupt Kv4.3 protein expression and K+ currents with variable effects on channel properties. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 22, 4986. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094986.
- C.-S. Chiang., S.-J. Fu., C.-L. Hsu, C.-J. Jeng, C.-Y. Tang, Y.-S. Huan, S.-C. Tang* (2021) Neuronal exosomes secreted under oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion presenting differentially expressed miRNAs and affecting neuronal survival and neurite outgrowth. NeuroMolecular Medicine. doi: 10.1007/s12017-020-08641-z.
- S.-J. Fu., M.-C. Hu, C.-T. Hsiao, A.-T. Cheng, T.-Y. Chen, C.-J. Jeng*, and C.-Y. Tang* (2021) Regulation of ClC-2 chloride channel proteostasis by molecular chaperones: correction of leukodystrophy-associated defect. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 22, 5859. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115859.
- S.-J. Fu, M.-C. Hu, Y.-J. Peng, H.-Y. Fang, C.-T. Hsiao, T.-Y. Chen, C.-J. Jeng*, C.-Y. Tang* (2020) CUL4-DDB1-CRBN E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Regulates Proteostasis of ClC-2 Chloride Channels: Implication for Aldosteronism and Leukodystrophy. Cells 9, 1332; doi:10.3390/cells9061332
- C.-J. Jeng, S.-J. Fu, C.-Y. You, Y.-J. Peng, C.-T. Hsiao, T.-Y. Chen, C.-Y. Tang* (2020) Defective gating and proteostasis of human CLC-1 chloride channel: molecular pathophysiology of myotonia congenital. Frontiers in Neurology Vol 11, Article 76; Doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00076
- C.-T. Hsiao, S.-J. Fu, Y.-T. Liu, Y.-H. Lu, C.-Y. Zhong, C.-Y. Tang, B.-W. Soong*, C.-J. Jeng* (2019) Novel SCA19/22-associated KCND3 mutations disrupt human KV4.3 protein biosynthesis and channel gating. Human Mutation 40:2088–2107. doi: 10.1002/humu.23865
- Y.-J. Peng, Y.-C. Lee, S.-J. Fu, Y.-C. Chien, Y.-F. Liao, T.-Y. Chen, C.-J. Jeng*, C.-Y. Tang* (2018) FKBP8 enhances protein stability of CLC-1 chloride channel at the plasma membrane. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 9: 3783, doi:10.3390/ijms19123783
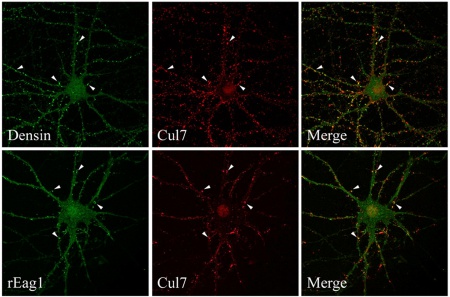
- P.-H. Hsu, Y.-T. Ma, Y.-C. Fang, J.-J. Huang, Y.-L. Gan, P.-T. Chang, G.-M. Jow, C.-Y. Tang*, C.-J. Jeng* (2017) Cullin 7 mediates proteasomal and lysosomal degradations of rat Eag1 potassium channels. Scientific Reports 7:40825, DOI: 10.1038.
- S.-J. Fu, C.-J. Jeng, C.-H. Ma, Y.-J. Peng, C.-M. Lee, Y.-C. Fang, Y.-C. Lee, S.-C. Tang, M.-C. Hu, C.-Y. Tang* (2017) Ubiquitin ligase RNF138 promotes episodic ataxia type 2-associated aberrant degradation of human CaV2.1 (P/Q-type) calcium channels. Journal of Neuroscience 37(9):2485–2503.
- P.-H. Hsu, Y.-C. Chiu, T.-F. Lin, C.-J. Jeng* (2016) Ca2+-binding protein centrin 4 is a novel binding partner of rat Eag1 K+ channels. FEBS Open Bio doi:10.1002/2211-5463.12045.
- Y.-C. Teng, C.-J. Jeng, H.-J. Huang, A. M.-Y. Lin (2015) Role of autophagy in arsenite-induced neurotoxicity: The involvement of alpha-synuclein. Toxicology Letters 233: 239-245.
- T.-F. Lin, G.-M Jow, H.-Y. Fang, S.-J. Fu, H.-H. Wu, M.-M. Chiu, C.-J. Jeng* (2014) The eag domain regulates the voltage-dependent inactivation of rat Eag1 K+ channels. PLoS ONE 9(10): e110423.
- T.-F. Lin, I-W. Lin, S.-C. Chen, H.-H. Wu, C.-S. Yang, H.-Y Fang, M.-M. Chiu, C.-J. Jeng* (2014) The subfamily-specific assembly of Eag and Erg K+ channels is determined by both the amino and the carboxyl recognition domains. Journal of Biological Chemistry 289(33):22815-22834.
- C.-C. Chuang, G.-M. Jow, H.-M. Lin, Y.-H. Weng, J.-H. Hu, Y.-J. Peng, Y.-C. Chiu, M.-M. Chiu, C.-J. Jeng* (2014) The punctate localization of rat Eag1 K+ channels. BMC Neuroscience 15:23.
- C.-K. Liao, C.-J. Jeng, H.-S. Wang, S.-H. Wang, J.C. Wu (2013) Lipopolysaccharide induces degradation of connexin43 in rat astrocytes via the ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway. PLoS ONE 8(11): e79350.
- P.-H. Hsu, S.-C. Miawa, C.-C. Chuang, P.-Y. Chang, S.-J. Fu, G.-M. Jow, M.-M. Chiu, C.-J. Jeng* (2012) 14-3-3theta is a Binding Partner of Rat Eag1 potassium Channels. PLoS ONE 7(7): e41203.
- S.-H. Yang, C.-C. Liao, Y. Chen, J.-P. Syu, C.-J. Jeng*, S.-M. Wang (2012) Daidzein induces neuritogenesis in DRG neuronal cultures. Journal of Biomedical Science 19:80.
- I.-H. Chen, J.-H. Hu, G.-M. Jow, C.-C. Chuang, T.-T. Lee, D.-C. Liu, C.-J. Jeng* (2011) The distal end of carboxyl-terminus is not essential for the assembly of rat Eag1 potassium channels. Journal of Biological Chemistry 286(31) 27183–27196.
- S.-H. Yang; C.-J. Jeng, C-H Chen, Y. Chen, Y.-C. Chen, and S.-M. Wang* (2011) Schisandrin enhances dendrite outgrowth and synaptogenesis in primary cultured hippocampal neurons. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture 91(4): 694–702.
受邀演講
- Proteostatic mechanism of neuronal K+ channels: Pathophysiological implications in neurological diseases, 國衛院細胞及系統醫學研究所, 7/14/2022.
- Molecular basis and pathological significance of K+ channel degradation, 成功大學醫學院細胞生物與解剖學研究所, 10/27/2021.
- Protein biosynthesis mechanisms of neuronal K+ channel degradation, 成功大學醫學院細胞生物與解剖學研究所, 5/1/2019.
- Proteostatic mechanism of Eag1 potassium channel, 29th Ion Channel Meeting, CANAUX IONIQUES, Sète, France, 9/10/2018.
- Regulation of ether-à-go-go potassium channel expression by RING E3 ubiquitin ligases and 14-3-3 proteins, 政治大學神經科學研究所, 5/22/2018.
- Regulation of ether-à-go-go potassium channel expression by ring E3 ubiquitin ligases, The 33th Joint Annual Conference of Biomedical Science, Taipei, Taiwan, 3/24/2018.
- Protein interaction mechanisms of Eag potassium channels, Internal Symposium in Osaka University, Osaka, Japan, 8/3/2017.
- Protein targeting and molecular assembly of ether-à-go-go potassium channels, The 31th Joint Annual Conference of Biomedical Science, Taipei, Taiwan, 3/26/2016.
- Protein interaction mechanisms of ether-à-go-go potassium channels, 國防大學醫學院生物及解剖學研究所, 12/8/2016.
- Molecular assembly of ether-à-go-go potassium channels, 陽明大學生理學研究所, 3/19/2015.
- Molecular assembly and protein association of ether-à-go-go potassium channels, 高雄榮民總醫院 教研部, 10/31/2014.
- Molecular assembly and protein association of Eag K+ channels, 生科院-週三中午有約, 6/5/2013.
- Structural and functional characterization of ether-à-go-go potassium channel, 輔仁大學醫學院基礎醫學研究所, 11/29/2012.
- Molecular assembly and protein association of neuronal potassium channels, The 26th Joint Annual Conference of Biomedical Sciences, 3/20/2011.